This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (CC BY).
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
The study of relative bioavailability of ocular suspension of 4-(5-methyl-1,3,4 oxadiazole-2-yl)-benzenesulfonamide in rabbits
1 Yaroslavl State Pedagogical University named after Ushinsky, Yaroslavl, Russia
2 Yaroslavl State Medical University, Yaroslavl, Russia
Correspondence should be addressed: Ilya I Yaichkov
Technopark str., 11/2, Yaroslavl, 150030, Russia; ur.liam@80_3991_ayli
Financing: the study was supported by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation (State assignment 1022051100011-8-3.1.5; 3.2.17 “Development of a drug for treatment of acute-angle glaucoma”).
Acknowledgement: the work was carried out in collaboration with the Scientific Department of the Institute of Pharmacy of Yaroslavl State Medical University, Yaroslavl.
Author contribution: Yaichkov II — experimental design development, analysis of rabbit plasma samples, performing statistical calculations, writing an article; Volkhin NN, Petukhov SS, Lazaryants OE — conducting the experiments on rabbits.
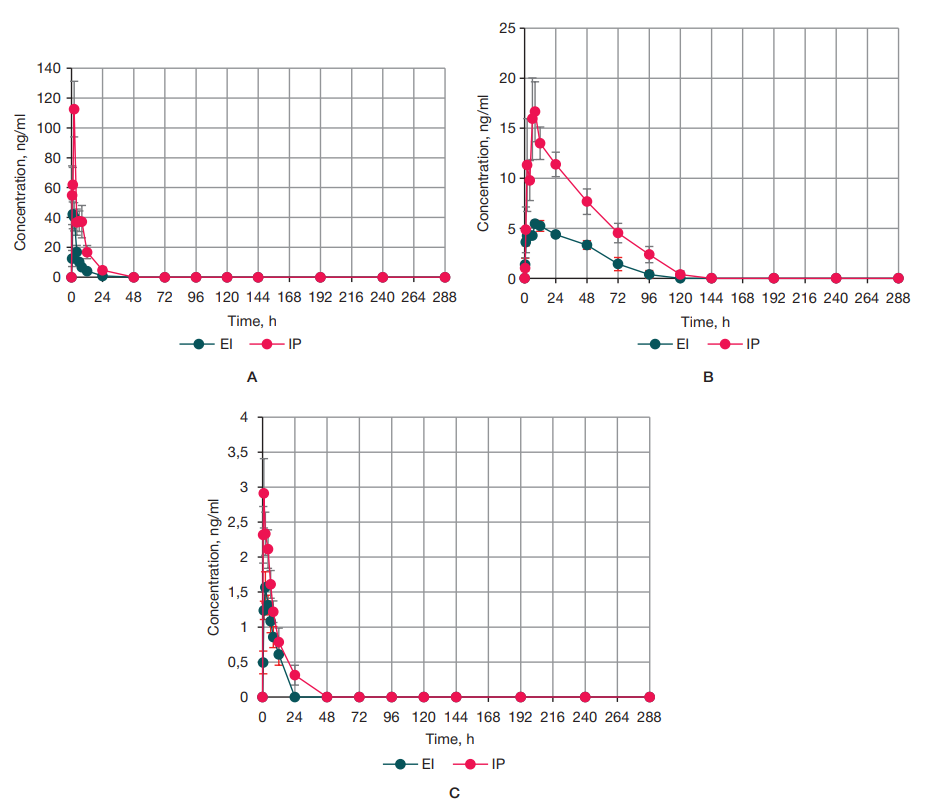
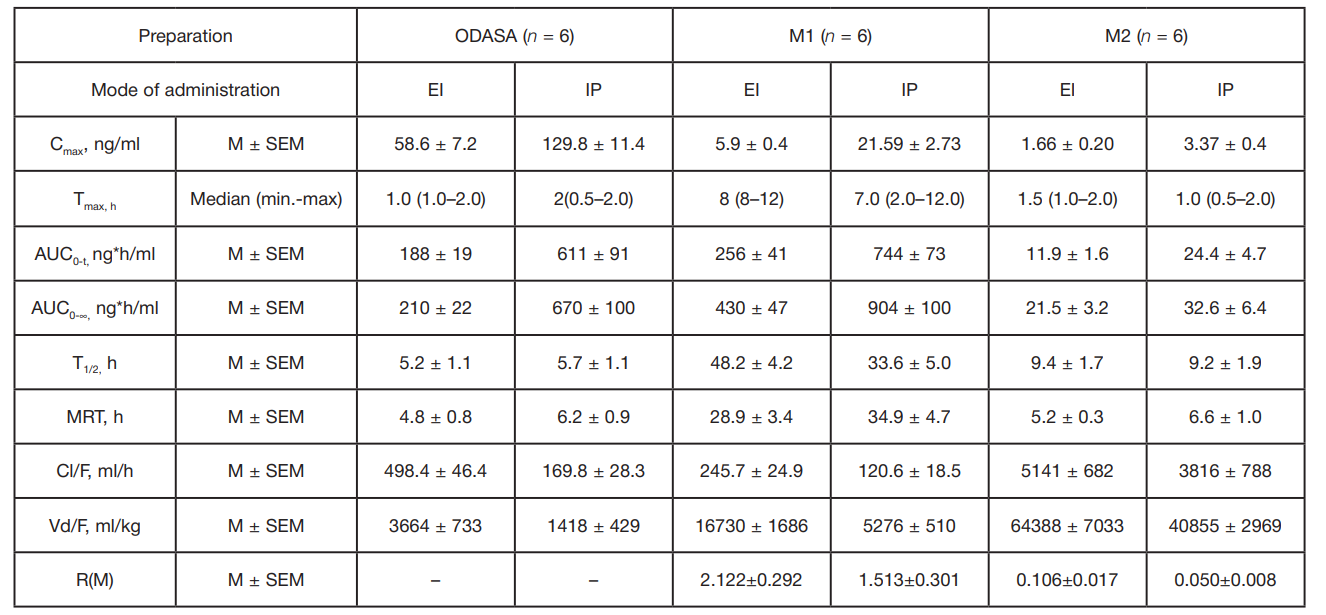
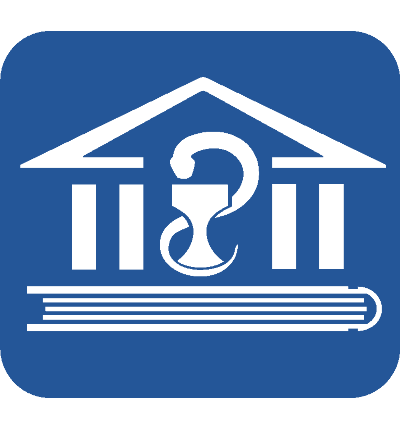
Compliance with ethical standards: the study was conducted in compliance with all ethical standards recommended in the Russian Federation. Rabbits were selected to evaluate the pharmacokinetic parameters and relative bioavailability of ODASA as other non-rodent species. The animals were kept in individual cages of a sufficient size. Access to water and mixed feed was available free-choice, except for 4 hours before administration and 2 hours after administration of the investigational preparation. The animals were housed at room temperatures of 20 °C, humidity of 40–65%, and a 12/12 h light–dark cycle. The experimental animals were under the supervision of a veterinarian throughout the experiment. Each group had a minimum allowable sample size for pharmacokinetic studies in the Russian Federation. This study was approved by the Independent Ethics Committee of the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education Yaroslavl State Medical University of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, Protocol No. 2 dated 04/20/2025.